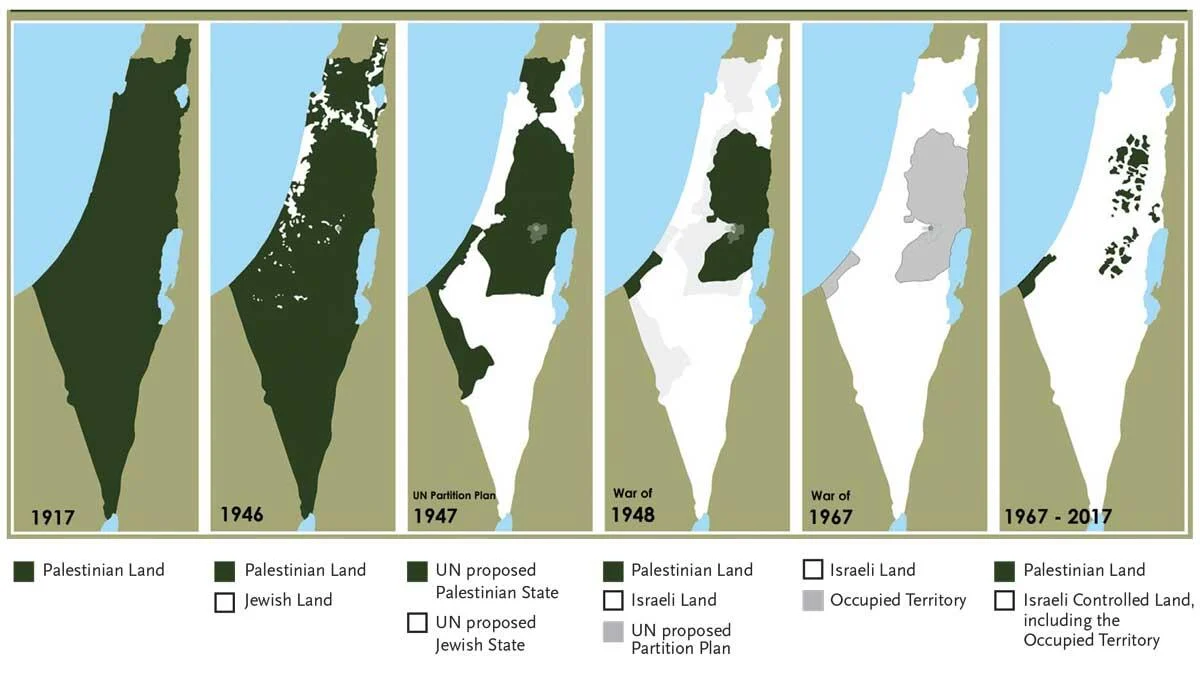
Palestinian Loss of Land Over Time

Timeline of Events and Conditions in Israel/Palestine
From the Middle Ages until the end of World War I the area we know as Palestine was part of the Ottoman Empire. Arabs (Muslim and Christian) made up most of the population of the area although there was a small Jewish population.
1897 Theodore Herzl organizes 1st Zionist Congress in Basel, Switzerland, in response to rising anti-Semitism in Europe. He begins a series of diplomatic initiatives intended to build support for a Jewish country.
1917 Balfour Declaration – a letter from the British foreign secretary, Arthur Balfour, to the wealthy Jewish banker Lord Rothschild proclaiming that “His Majesty’s government view with favor the establishment in Palestine of a National Home for the Jewish people.”
1918 End of World War I – Palestine becomes a British Mandate, a western euphemism for nominally sovereign states under European tutelage sanctioned by the League of Nations.
Under the British Mandate
Until the eve of the Second World War, the British administratively, politically, and militarily established the basis for a Jewish state in Palestine. Jewish immigration into Palestine increases.
1932 Hitler seizes power in Germany, ultimately leading to Holocaust.
1945 End of World War II – Immigration into Israel becomes a flood of Holocaust survivors and other European Jews. Palestine is still under the British Mandate.
The Mandate Ends – Israel is established
1947 UN General Assembly decides on partition of Palestine into Jewish and Arab states with Jerusalem as an international city. Arab nations don’t agree. War breaks out.
1948 Jewish armies defeat the Arab armies. Jordan claims the West Bank and East Jerusalem, including the Old City and the Temple Mount. The Egyptians occupy Gaza and the Sinai.
1948 May 14, Ben-Gurion announces the birth of Israel. Within minutes President Truman recognizes the new state of Israel. Palestinians experience the Nakba, with many uprooted, killed, expelled, hundreds of their villages razed.
1949 Armistice Agreement establishes demarcation lines between the armies of Israel and those of its neighbors. This becomes the “Green Line”.
1964 Palestine Liberation Organization founded, recognized as the "sole legitimate representative of the Palestinian people" by over 100 states with which it holds diplomatic relations, and has enjoyed observer status at the United Nations since 1974, considered to be a terrorist organization by the U.S. and Israel until the Madrid Conference in 1991. In 1993 the PLO recognizes Israel's right to exist in peace, accepts UN Security Council resolutions 242 and 338, and rejects "violence and terrorism"; in response, Israel officially recognized the PLO as the representative of the Palestinian people.
1967 Six Day War – The Soviets warn President Nassar of Egypt that an Israeli invasion of Syria is imminent. Nassar was warned by the Soviets that an Israeli invasion of Syria was imminent. Nasser blockades the Straits of Tiran, providing Israel with a ‘casus belli’. Israel launches a surprise attack and acquires control of the Sinai, Golan Heights, West Bank, East Jerusalem. Once more, hundreds of thousands of Palestinians flee or are expelled from their homes. Israel’s military superiority strengthens the pro-Israeli orientation of United States policy.
Israel begins moving Israeli civilians into housing enclaves called ‘settlements’ on Palestinian land it occupied during this war.
On June 8, the USS Liberty, an American intelligence-gathering ship, is attacked by Israeli air and naval forces. Thirty-four U.S. sailors are killed, 171 wounded. Israel insists that this was a tragic mistake. Initial outrage in Washington turns into official silence. Congress doesn’t hold hearings or investigate.
1973 Yom Kippur War – Egypt and Syria initiate hostilities on October 6 with the goal of regaining their lands occupied by Israel. When things didn’t go well for the Israelis, the U.S. intervened by resupplying Israel with military hardware while the Soviets resupplied the Arabs. President Nixon believed that U.S. Cold War prestige was tied to Israeli success on the battlefield against the Soviet-sponsored Arabs. He also hoped for increased leverage with Israel in the aftermath of the war so that it could be “dragged kicking and screaming to the table.”
1978 Camp David Accords – An agreement between Egypt’s President Sadat and Israel’s Prime Minister Begin, signed at the White House, witnessed by President Carter, that results in a peace treaty between the two countries and Israel’s withdrawal from the Sinai.
1982 Israel invades Lebanon, forcing PLO's departure. Massacre of Palestinians in the Sabra and Shatila camps in Beirut by Israel's Christian Phalangist allies.
1987 First Intifada begins, lasting until 1993. A Palestinian uprising against the Israeli occupation of the Palestinian Territories, triggered by a traffic incident when an Israeli Defense Forces' (IDF) truck collided with a civilian car, killing four Palestinians. A protest movement arose in the wake of the incident, involving a two-fold strategy of unarmed resistance and civil disobedience, consisting of general strikes, boycotts of Israeli Civil Administration institutions in the Gaza Strip and the West Bank, an economic boycott consisting of refusal to work in Israeli settlements on Israeli products, refusal to pay taxes, refusal to drive Palestinian cars with Israeli licenses, graffiti, barricading, and widespread throwing of stones and Molotov cocktails at the IDF and its infrastructure within the Palestinian territories.
Israel deployed some 80,000 soldiers and initially fired live rounds, killing a large numbers of Palestinians. In the first 13 months, 332 Palestinians and 12 Israelis were killed. Given the high proportion of children, youths and civilians killed, it then adopted a policy of 'might, power, and beatings,' namely "breaking Palestinians' bones". The global diffusion of images of soldiers beating adolescents with clubs then led to the adoption of firing semi-lethal plastic bullets.
1993 The Oslo Accords, completed in 1995. Israel recognizes the PLO; the PLO formally recognizes Israel. The accords spell out a ‘declaration of principles’ that created the Palestinian Authority to administer islands of Palestinian self-rule, surrounded by either Israeli settlements or Israeli military installations. Israel continues to expropriate Palestinian land, to build Jewish-only bypass roads and colonies, and to fragment the West Bank into isolated pockets of Palestinian life hemmed in by Jewish Israeli settlers and soldiers.
2000 Camp David – Israeli Prime Minister Barak and Arafat meet with President Clinton. Arafat is presented with a take-it-or-leave-it deal that purported to offer the promise of an independent, demilitarized Palestinian state. But Israel demanded continued control of Palestinian airspace, West Bank water aquifers, a prolonged lease of land along the border with Jordan, the annexation of land that included major Jewish settlements, sovereignty over most of Jerusalem and the bypass roads on the West Bank. Arafat refused this deal which is now hailed as Israel’s most “generous offer”.
2000 Second Intifada, the second Palestinian uprising against Israeli occupation, lasts until 2005. It begins when Israeli Prime Minister Ariel Sharon makes a visit to Haram-al-Sharif or the Temple Mount and develops into a period of intensified Israeli-Palestinian violence. Both sides cause high numbers of casualties among civilians as well as combatants: the Palestinians by numerous suicide bombing and gunfire; the Israelis by tank and gunfire and air attacks, by numerous targeted killings, and by harsh reactions to demonstrations. The death toll, including both military and civilian, is estimated to be about 3,000 Palestinians and 1,000 Israelis, as well as 64 foreigners.
2002 The Israeli parliament decides to build the wall (separation barrier).
2004 International Court of Justice rules that the route of Israel’s “separation barrier” violates international law.
2005 Israel disengages from Gaza, dismantling settlements and security structures. Settlers are compensated and resettled. Hamas governs Gaza while Israel continues to control borders, air space, etc.
2006 Hamas, the Palestinian Islamist fundamentalist socio-political organization with an associated paramilitary force, defeats Fatah, leading secular Palestinian political party and largest faction of the PLO, in a parliamentary election. The election is not recognized in several quarters. Hamas assumes control of Gaza while Fatah rules the West Bank.
2008 Operation Cast Lead, a three-week armed conflict between Palestinians in the Gaza Strip and Israel that began on 27 December 2008 and ended on 18 January 2009. Israel's stated goal was to stop rocket fire into Israel and weapons smuggling into the Gaza strip. Israeli forces attacked police stations, military targets including weapons caches and suspected rocket firing teams, as well as political and administrative institutions in the opening assault, striking in densely populated cities. After hostilities broke out, Palestinian groups fired rockets in response to what they characterized as "massacres".
2014 Hamas and Fatah agree to form a unity government, alarming the Israelis. Tensions between Hamas and Fatah continue.
2014 Operation Protective Edge - A military operation launched by Israel in the Hamas-ruled Gaza Strip. Results after seven weeks of Israeli bombardment, Palestinian rocket attacks, and ground fighting:
Gazans: between 2,142 and 2,310 killed, between 10,626 and 10,895 wounded (including 3,354 children)
Israelis: 66 soldiers, 5 civilians killed, 469 soldiers, 261 civilians injured.
2015 Palestinian unity government was dissolved.
2016 US approves a military aid package worth $38 billion over next 10 years for Israel, largest such deal in US history. Previous pact, set to expire in 2018, saw Israel get $3.1 billion annually.
2018 President Trump moves US embassy from Tel Aviv to Jerusalem and eliminates UNRWA funding.
Gazans begin weekly Great March for Return demonstrations at the boundary with Israel. By the end of the year over 250 Palestinians had been killed and over 20,000 injured. Many survivors lost their limbs after being shot by Israeli soldiers. Human rights organizations condemned Israel’s “shoot-to-kill-or-maim” policy.
Israeli Knesset adopts the 'Nation-State Law' which specifies the State of Israel as the nation-state of the Jewish people.
2019 USAID assistance in the West Bank and Gaza ceases. Great March for Return continues.
